Computer Memory System Overview
An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
Some popular Operating Systems include Linux Operating System, Windows Operating System, VMS, OS/400, AIX, z/OS, etc.
Definition
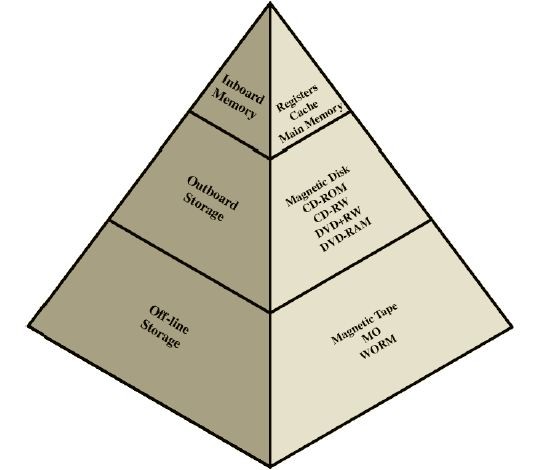
Computer Memory. The system memory is the place where the computer holds current programs and data that are in use. There are various levels of computer memory, including ROM, RAM, cache, page and graphics, each with specific objectives for system operation. This section focuses on the role of computer memory, and the technology behind it. Ran on a computer with 32,000 36-bit words of main memory, with the resident monitor consuming 5000 of that To simplify both the monitor and memory management a program was always loaded to start at the location of the 5000th word Time Slicing System clock generates interrupts at a rate of approximately one every 0.2 seconds.
An operating system is a program that acts as an interface between the user and the computer hardware and controls the execution of all kinds of programs.
Following are some of important functions of an operating System.
- Memory Management
- Processor Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Security
- Control over system performance
- Job accounting
- Error detecting aids
- Coordination between other software and users
Memory Management
Memory management refers to management of Primary Memory or Main Memory. Main memory is a large array of words or bytes where each word or byte has its own address.
Main memory provides a fast storage that can be accessed directly by the CPU. For a program to be executed, it must in the main memory. An Operating System does the following activities for memory management −
Keeps tracks of primary memory, i.e., what part of it are in use by whom, what part are not in use.
In multiprogramming, the OS decides which process will get memory when and how much.
Allocates the memory when a process requests it to do so.
De-allocates the memory when a process no longer needs it or has been terminated.
Processor Management
In multiprogramming environment, the OS decides which process gets the processor when and for how much time. This function is called process scheduling. An Operating System does the following activities for processor management −
Keeps tracks of processor and status of process. The program responsible for this task is known as traffic controller.
Allocates the processor (CPU) to a process.
De-allocates processor when a process is no longer required.
Device Management
An Operating System manages device communication via their respective drivers. It does the following activities for device management −
Keeps tracks of all devices. Program responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller.
Decides which process gets the device when and for how much time.
Allocates the device in the efficient way.
De-allocates devices.
File Management
A file system is normally organized into directories for easy navigation and usage. These directories may contain files and other directions.
An Operating System does the following activities for file management −
Keeps track of information, location, uses, status etc. The collective facilities are often known as file system.
Decides who gets the resources.
Allocates the resources.
De-allocates the resources.
Other Important Activities
Following are some of the important activities that an Operating System performs −
Security − By means of password and similar other techniques, it prevents unauthorized access to programs and data.
Control over system performance − Recording delays between request for a service and response from the system.
Job accounting − Keeping track of time and resources used by various jobs and users.
Error detecting aids − Production of dumps, traces, error messages, and other debugging and error detecting aids.
Coordination between other softwares and users − Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, assemblers and other software to the various users of the computer systems.
What are the different types of computer memory? Computers are very important parts of our daily lives. These computers work by the help of computer memory as they safe keep the data while they have not been processed yet. There are many different types of computer memory that can be used in different technologies. No matter how you want to use your computer, you can surely be able to enjoy them better if you have a better type of memory in it.
Hard Disk Drive. The hard disk drives are among the most common types of computer memory. They can store the data and information long term as this is where you store your music, games, documents, and the like. Hard drives work much like records. They are spinning platters that have arms with head to touch the different parts of it. When the head is at a certain location, data and information are either being written or deleted from that area of the hard drive. The largest hard drives available these days are as big as 2 terabytes and can store information up to 70 megabytes every second.
RAM. RAM stand for Random Access Memory. These are electronic types of computer memory that accesses any information any time. These types of memory work reversely like tapes. Since they are electronic, there are no arms, heads and spinning involved. RAM work really fast as they are the ones who bring the information to the brain to be processed. However, all the information and data stored here are short term as after they are processed the RAM frees itself so that more information can be processes by the CPU after.
Flash Memory. Flash memories are types of computer memory that works like RAM but are stable. Even when there is no power, the information and data saved in them are kept safe and secure. They cannot, however, keep as much data and information like the hard disk drive. These are very small and portable devices therefore not much hardware is available, hence the small storage space. At present, the biggest flash memory drives can only hold up to 32 GB of data. Unfortunately, flash memories are slow. The fastest of the flash memories can only read up to 22 megabytes every second.
Tape Drives. Tape drives are types of computer memory that work like tapes or audio cassettes. They have ribbons and spools, where the data and information you would like to store are saved with the ribbon’s polarity. These tape drives are mostly used by medium to large organizations as they offer long term and stable storage.
Lastly, we have the CDROM memory. These are the types of computer memory that are permanent and portable. These types of computer memory works like records and hard drives. However, instead of the head and arm, a laser light writes and reads the information on the CDs and DVDs to interpret it and display them in the monitor. The best thing about the CDROM memory is that they are very durable, especially when compared with all other types of memory.
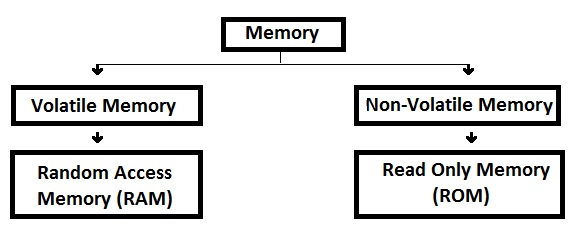
Computer memory is a location in which various data is stored in a computer system. The operating systems, software, user documents etc. are stored in the computer memory. There are different types of computer memory which may be classified according to how they store data, accessibility etc. When choosing a computer memory, some of the factors which must be put into consideration include the speed at which data can be stored and accessed besides the capacity of the memory location. Some have the ability to store data permanently while others lose all their data as soon as they lose power; it all depends on the type of computer memory being used.
Since the invention of computers, different types of computer memory have invented to achieve high levels of efficiency. They include:
– Random Access Memory (RAM)
– Read Only Memory (ROM)
– Cache memory
– Computer hard drives
– Flash memory
RAM: This is the main memory of any computer systems. Processors normally access information in a given order. The information must be loaded in the RAM so that the processor can access it. Therefore the co-ordination between these types of computer memory plays a significant role in computer operations. Data in computer RAM can be accessed in order as long as it has been loaded. A higher RAM performance normally translates to a higher performance of the computer system.
These types of computer memory can be classified further as:
– Dynamic RAM (DRAM) – The maintenance of its state will always depend on the presence of electricity. Its access time normally ranges from 60 to 70 nanoseconds.
– Static RAM (SRAM) – Its access time is less than 60 nanoseconds.
– Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM) – It considerably faster than the DRAM with an access speed of less than 20 nanoseconds.
ROM: Unlike the RAM, the data present in the ROM cannot be changed thus being a non-volatile (it will always keep its contents regardless whether there’s power or not). These types of computer memory are used to describe different media or memory that can only be read e.g. the DVD-ROM and CD-ROM. ROM is normally sustained by a battery in the computer system and it allows the computer to boot any time it is required to do so.
This type of computer memory can be classified into different categories which include:
– Programmable ROM (PROM) – It store programs and cannot be erased.
– Erasable PROM (EPROM) – Can always be erased by exposure to UV light.
– Electrically EPROM (EEPROM) – Can be erased by exposing it to an electric charge.
Computer Hard Drives
These types of computer memory exist in different types which include the Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA), Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA), the Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) which has a high data access which normally goes up to 10,000 – 15,000 rpm and the solid state drives which are faster an more durable as they don’t have the rotating magnetic disks that the other computer hard drives have.
Other types of computer memory include cache memory which is a type of RAM with a high response rate as far as data accessibility is concerned and flash memory which can be erased and programmed as per the user’s needs. They include the USB flash and the memory cards.
Computer Memory System Overview Template
These different types of computer memory have different purposes, none smaller than the other in the grand scheme of things. But in general, the RAM and the hard disc memory are the two types of computer memory that of great interest when listing the specs of a computer. Proper knowledge of the significance of these memories therefore means that one can make a good choice when buying a comp.